Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138017_1 - 138017_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The Casimir effect is a quantum phenomenon induced by the zero-point energy of relativistic fields confined in a finite-size system. This effect for photon fields has been studied for a long time, while the realization of counterparts for fermion fields in Dirac/Weyl semimetals is an open question. We theoretically demonstrate the typical properties of the Casimir effect for relativistic electron fields in Dirac/Weyl semimetals and show the results from an effective Hamiltonian for realistic materials such as Cd As
As and Na
and Na Bi. We find an oscillation of the Casimir energy as a function of the thickness of the thin film, which stems from the existence of Dirac/Weyl nodes in momentum space. Experimentally, such an effect can be observed in thin films of semimetals, where the thickness dependence of thermodynamic quantities is affected by the Casimir energy.
Bi. We find an oscillation of the Casimir energy as a function of the thickness of the thin film, which stems from the existence of Dirac/Weyl nodes in momentum space. Experimentally, such an effect can be observed in thin films of semimetals, where the thickness dependence of thermodynamic quantities is affected by the Casimir energy.
Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review Research (Internet), 5(2), p.L022054_1 - L022054_6, 2023/06
The Casimir effect is a fundamental quantum phenomenon induced by the zero-point energy for a quantum field. It is well-known for relativistic fields with a linear dispersion relation, while its existence or absence for nonrelativistic fields with a quadratic dispersion is an unsettled question. Here, we investigate the Casimir effects for various dispersion relations on the lattice. We find that Casimir effects for dispersions proportional to an even power of momentum are absent in a long distance under some types of boundary conditions, while a remnant of the Casimir effect survives in a short distance. The concepts of such absence and remnants of Casimir effect help us to understand observables in finite-size materials with quantum fields on the lattice, such as thin films, narrow nanoribbons, and short nanowires. In terms of this effect, we also give a reinterpretation of the Casimir effect for massive fields.
Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 430, p.379_1 - 379_9, 2023/04
The conventional Casimir effect has been studied in the continuous spacetime, but to elucidate its counterpart in the lattice space is an important subject. Here, we discuss various types of Casimir effects for quantum fields on the lattice. By using a definition of the Casimir energy on the lattice, we show that the Casimir effect for the Wilson fermion is similar to that for the continuous Dirac fermion. We apply our definition to an effective Hamiltonian describing Dirac semimetals, such as Cd As
As and Na
and Na Bi, and find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy as a function of film thickness of semimetals. We also study contributions from Landau levels under magnetic fields and the Casimir effect for nonrelativistic particle fields on the lattice.
Bi, and find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy as a function of film thickness of semimetals. We also study contributions from Landau levels under magnetic fields and the Casimir effect for nonrelativistic particle fields on the lattice.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_23, 2021/06
The Casimir effect arises from the zero-point energy of particles in momentum space deformed by the existence of two parallel plates. For degrees of freedom on the lattice, its energy-momentum dispersion is determined so as to keep a periodicity within the Brillouin zone, so that its Casimir effect is modified. We study the properties of Casimir effect for lattice fermions, such as the naive fermion, Wilson fermion, and overlap fermion based on the M bius domain-wall fermion formulation, in the
bius domain-wall fermion formulation, in the 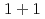 ,
, 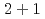 , and
, and 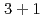 dimensional spacetime with the periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. An oscillatory behavior of Casimir energy between odd and even lattice size is induced by the contribution of ultraviolet-momentum (doubler) modes, which realizes in the naive fermion, Wilson fermion in a negative mass, and overlap fermions with a large domain-wall height. Our findings can be experimentally observed in condensed matter systems such as topological insulators and also numerically measured in lattice simulations.
dimensional spacetime with the periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. An oscillatory behavior of Casimir energy between odd and even lattice size is induced by the contribution of ultraviolet-momentum (doubler) modes, which realizes in the naive fermion, Wilson fermion in a negative mass, and overlap fermions with a large domain-wall height. Our findings can be experimentally observed in condensed matter systems such as topological insulators and also numerically measured in lattice simulations.
Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physics Letters B, 809, p.135713_1 - 135713_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:75.97(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose a definition of the Casimir energy for free lattice fermions. From this definition, we study the Casimir effects for the massless or massive naive fermion, Wilson fermion, and (M bius) domain-wall fermion in 1+1 dimensional spacetime with the spatial periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. For the naive fermion, we find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy, which is caused by the difference between odd and even lattice sizes. For the Wilson fermion, in the small lattice size of
bius) domain-wall fermion in 1+1 dimensional spacetime with the spatial periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. For the naive fermion, we find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy, which is caused by the difference between odd and even lattice sizes. For the Wilson fermion, in the small lattice size of 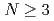 , the Casimir energy agrees very well with that of the continuum theory, which suggests that we can control the discretization artifacts for the Casimir effect measured in lattice simulations. We also investigate the dependence on the parameters tunable in M
, the Casimir energy agrees very well with that of the continuum theory, which suggests that we can control the discretization artifacts for the Casimir effect measured in lattice simulations. We also investigate the dependence on the parameters tunable in M bius domain-wall fermions. Our findings will be observed both in condensed matter systems and in lattice simulations with a small size.
bius domain-wall fermions. Our findings will be observed both in condensed matter systems and in lattice simulations with a small size.
 mesons as a probe of Casimir effect for chiral symmetry breaking
mesons as a probe of Casimir effect for chiral symmetry breakingIshikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 100(3), p.034016_1 - 034016_14, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.59(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We propose  mesons as probes to investigate finite-volume effects for chiral symmetry breaking at zero and finite temperatures. By using the 2+1-flavor linear sigma model with constituent light quarks, we analyze the Casimir effects for the
mesons as probes to investigate finite-volume effects for chiral symmetry breaking at zero and finite temperatures. By using the 2+1-flavor linear sigma model with constituent light quarks, we analyze the Casimir effects for the  mean fields; the chiral symmetry is rapidly restored by the antiperiodic boundary for light quarks, and the chiral symmetry breaking is catalyzed by the periodic boundary. We also show the phase diagram of the
mean fields; the chiral symmetry is rapidly restored by the antiperiodic boundary for light quarks, and the chiral symmetry breaking is catalyzed by the periodic boundary. We also show the phase diagram of the  mean fields on the volume and temperature plane. For
mean fields on the volume and temperature plane. For  mesons, we employ an effective model based on the chiral-partner structure, in which the volume dependence of
mesons, we employ an effective model based on the chiral-partner structure, in which the volume dependence of  mesons is induced by the
mesons is induced by the  mean fields. We find that
mean fields. We find that 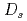 mesons are less sensitive to finite volume than
mesons are less sensitive to finite volume than  mesons, which is caused by the insensitivity of
mesons, which is caused by the insensitivity of 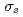 mean fields. An anomalous mass shift of
mean fields. An anomalous mass shift of  mesons at high temperature with the periodic boundary will be useful in examinations with lattice QCD simulations. The dependence on the number of compactified spatial dimensions is also studied.
mesons at high temperature with the periodic boundary will be useful in examinations with lattice QCD simulations. The dependence on the number of compactified spatial dimensions is also studied.
Tomota, Yo*; Sekido, Nobuaki*; Xu, P. G.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Shinohara, Takenao; Su, Y. H.; Taniyama, Akira*
Tetsu To Hagane, 103(10), p.570 - 578, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.55(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Kamijo, Eiji*; Aoi, Yoshifumi*; Hisa, Masaaki*; Utsumi, Wataru; Watanuki, Tetsu; Yamaguchi, Koji*
Diamond and Other Carbon Materials 3, p.97 - 104, 2003/05
no abstracts in English
Motoki, Ryozo; Nemoto, Masahiro*
JAERI-Tech 2002-030, 46 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
 ion source for the high intensity proton Linac
ion source for the high intensity proton LinacOguri, Hidetomo; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Namekawa, Yuya*; Shimooka, Takashi*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 73(2), p.1021 - 1023, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:64.47(Instruments & Instrumentation)At JAERI, a high intensity proton accelerator with a beam power of 1 MW has been proposed to pursue the nuclear-particle physics, materials and life sciences and R&D for nuclear transformation. A negative hydrogen ion source for the accelerator is required to extract a peak beam current of more than 60 mA with a normalized emittance of 0.15 pimm.mrad (rms). We have designed and tested a volume production type negative ion source to accumulate experimental data to fulfill the requirement for the accelerator. The source plasma is produced by an arc discharge using tungsten filaments. The cesium vapor is introduced into the arc chamber to enhance the beam current. The beam extractor consists of three electrodes with a single aperture of 8 mm in diameter. The negative ion beam current of 40 mA was achieved with a duty factor of 5 % at the beam energy and arc discharge power of 70 keV and 30 kW, respectively. The beam current increased linearly with the arc power in the cesium operation. The beam test by using a more powerful arc power supply is in progress.
Saegusa, Jun
Hokeikyo Nyusu, (28), p.2 - 5, 2001/10
no abstracts in English
Miyoshi, Takahiro; Kusano, Kanya*
Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(A6), p.10723 - 10742, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:44.09(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 -irradiation on positronium formation in polymers at low temperature
-irradiation on positronium formation in polymers at low temperatureShantarovich, V. P.*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Kerdina, I. B.*; Gustov, V. W.*; Arzhakov, M. S.*
Materials Science Forum, 363-365, p.352 - 354, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Hendri, J.*; Hiroki, Akihiro*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru; Katakai, Ryoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 61(2), p.155 - 161, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.6(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sato, Haruo
JNC TN8410 2001-003, 40 Pages, 2001/01
A program (TDROCK1.FOR) for simulation and analysis of through-diffusion experiments for a single layer of diffusion media was developed. This program was made by Pro-Fortran language, which was suitable for scientific and technical calculations, and relatively easy explicit difference method was adopted for an analysis. In the analysis, solute concentration in the tracer cell as a function of time that we could not treat to date can be input and the decrease in the solute concentration as a function of time by diffusion from the tracer cell to the measurement cell, the solute concentration distribution in the porewater of diffusion media and the solute concentration in the measurement cell as a function of time can be calculated. In addition, solution volume in both cells and diameter and thickness of the diffusion media are also variable as an input condition. This simulation program could well explain measured result by simulating solute concentration in the measurement cell as a function of time for case which apparent and effective diffusion coefficients were already known. Based on this, the availability and applicability of this program to actual analysis and simulation were confirmed. This report describes the theoretical treatment for the through-diffusion experiments for a single layer of diffusion media, analytical model, an example of source program and the manual.
Shirai, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Itakura, Hirofumi*; Takase, Keizo*
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-040, 214 Pages, 2001/01
no abstracts in English
 -ray efficiency curves for volume samples by the combination of Monte Carlo simulations and point source calibration
-ray efficiency curves for volume samples by the combination of Monte Carlo simulations and point source calibrationSaegusa, Jun; Oishi, Tetsuya; Kawasaki, Katsuya; Yoshizawa, Michio; Yoshida, Makoto; Sawahata, Tadahiro*; Honda, Tetsutaro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 37(12), p.1075 - 1081, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Kritmaitree, P.*; Akiyama, Mitsunobu*; Hino, Ryutaro; Kaminaga, Masanori; Terada, Atsuhiko*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 37(11), p.996 - 998, 2000/11
no abstracts in English